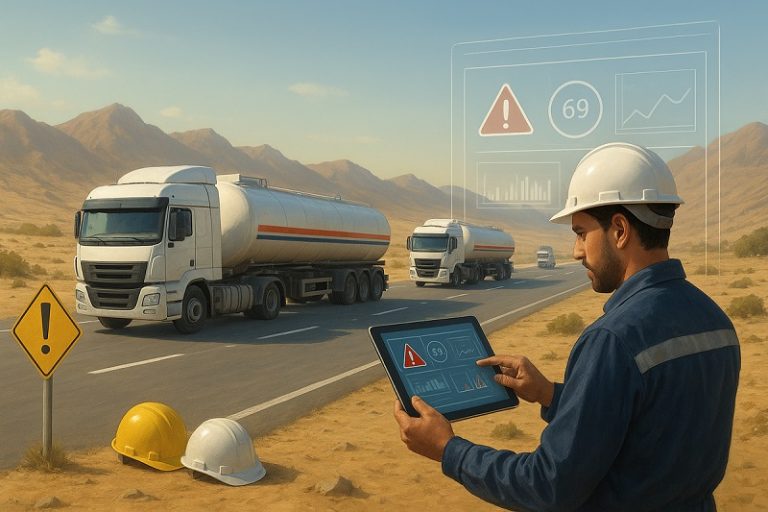
The transportation of petroleum products is among the most sensitive and high-risk segments of the energy supply chain in any country. Beyond its technical and economic dimensions, it encompasses complex aspects of safety, environmental protection, and social responsibility.
In this context, risk management emerges as a central pillar of operational sustainability. Its purpose is to identify, assess, control, and minimize the likelihood of incidents that may threaten human life, organizational assets, or the environment.
Nature of Risk in Road Fuel Transportation
Risk in fuel transport operations arises from a combination of human, technical, environmental, and organizational factors.
The most significant categories of risk in this field include:
Technical Risks: Brake failures, excessive tank pressure, or malfunctioning transfer equipment.
Human Risks: Driver fatigue, poor decision-making, or lack of safety awareness.
Environmental Risks: Weather conditions, road hazards, or traffic congestion.
Organizational Risks: Inadequate supervision, poor coordination between departments, or lack of emergency protocols.
Effective risk management requires a systematic and preventive approach—identifying potential hazards and designing control mechanisms before incidents occur.
Core Principles of Risk Management in Fuel Transport
Risk management is a continuous, multi-stage process that must be integrated into every phase of fuel transportation operation. The essential stages include:
Risk Identification: Collecting operational data, reviewing past incidents, and conducting field inspections.
Risk Assessment and Prioritization: Evaluating the probability and impact of potential hazards to focus on critical risks.
Risk Control and Mitigation: Implementing safety systems, professional training, and continuous fleet monitoring.
Monitoring and Review: Periodically assessing the effectiveness of controls and updating risk management plans.
These stages, when implemented in accordance with international standards such as ISO 31000 and ADR, ensure a safer, more reliable, and environmentally responsible transport operation.
Applied Examples in Risk Management
In recent years, leading companies in the petroleum logistics sector have adopted advanced risk management technologies, including:
Remote alarm and monitoring systems to prevent leakage or overheating;
Driver behavior and fatigue monitoring sensors to detect unsafe conditions in real time;
Fleet data analytics to predict equipment failures before they occur.
Such tools allow for proactive decision-making and significantly reduce both financial and human losses.
Hormozgan Fuel Tankers Company’s Commitment to Risk Management
Recognizing the importance of risk management in safe and sustainable operations, Hormozgan Fuel Tankers Company has implemented a comprehensive and structured risk management program.
Key initiatives include:
Establishing an intelligent fleet monitoring system for real-time tracking and performance analysis of tankers;
Conducting specialized training courses for drivers and technical staff on safety and emergency response;
Equipping tankers with modern protective devices;
Collaborating closely with the Road Maintenance and Transportation Organization, the National Iranian Oil Products Distribution Company, and the Department of Environment to align with national and international safety standards.
These initiatives reflect Hormozgan Fuel Tankers Company’s commitment to protecting human life, environmental integrity, and national assets through responsible and forward-thinking risk management.
Conclusion
Risk management in road transportation of petroleum products is not merely a technical requirement—it is a corporate culture.
Organizations that adopt a preventive rather than reactive approach can enhance safety, operational resilience, and public trust.
With its scientific and experience-based approach, Hormozgan Fuel Tankers Company stands as a model of professional risk management in Iran’s fuel transportation sector, contributing to a safer and more sustainable national energy network.
Keywords
Risk management, fuel transportation, petroleum logistics, road safety, ISO 31000, ADR, operational safety, fuel tanker operations, Hormozgan Fuel Tanker Company, driver safety, risk assessment, crisis management
References
1-ISO 31000: Risk Management – Guidelines, International Organization for Standardization, 2023.
2-ADR 2023 – European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road, UNECE.
3-FMCSA (U.S. Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration), Risk-Based Safety Management Systems, 2022.
4-Ministry of Petroleum, Iran – Safety Regulations for Fuel Transportation, 2024.
5-Internal Reports, Safety, Training, and Operations Departments, Hormozgan Fuel Tanker Company, 2024.